Journalism — particularly newspapers — has been trying to shift to video for years, often sputtering like a ’57 Chevy with a bad carburetor.
And for good reason.
The inverted pyramid still figures prominently in J schools across the country.
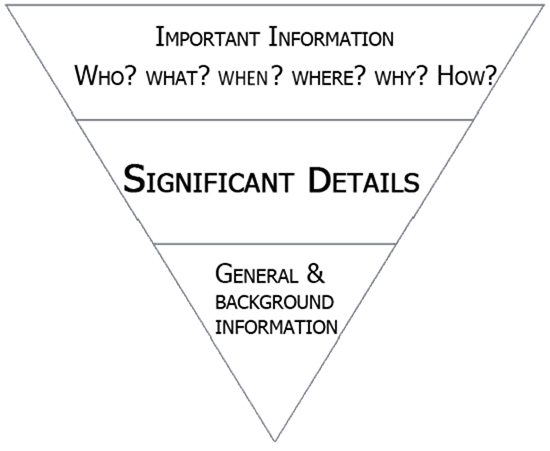 If you’re pounding out news stories for the Daily Planet, the inverted pyramid serves you well. But applying the inverted pyramid to video isn’t going to hold the viewer’s interest, much less prompt hey-you-gotta-check-this-out sharing across social channels.
If you’re pounding out news stories for the Daily Planet, the inverted pyramid serves you well. But applying the inverted pyramid to video isn’t going to hold the viewer’s interest, much less prompt hey-you-gotta-check-this-out sharing across social channels.
The skill set for video is different.
The mentality — a spoonful of entertainment helps the storytelling go down — is different.
Equally important, video calls for the journalist to take a collaborative approach to the storytelling. It’s not enough to think in terms of visuals and actions that advance the story. The journalist must team with producers, videographers, graphic designers, audio engineers, illustrators and other specialists to bring video to life.
The New York Times gets this concept. Back in February, NYT Executive Editor Dean Baquet shared in a note to the staff:
In ways large and small, the newsroom is experimenting and adapting as we move into our digital future. We are revamping our video unit. The news hub is beginning to free desks to focus on coverage without being consumed by print deadlines. We have begun a desk-by-desk digital training regimen. We have gone from being largely unaware of our audience’s changing habits to making them an integral part of our daily conversations. In our news meetings we talk of coverage, regardless of platform. More and more we discuss how to highlight all kinds of stories — video, multimedia, the politics desk’s great voices feature — that are more digital than print. We debate openly and freely as we experiment with new ways of telling stories.
What really brings this home is the recent NYT video, “How China Is Changing Your Internet.”
It’s a great example of the convergence of serious journalism and entertainment.
The opening narration lays down the serious tack:
If you’re sitting in the United States or Europe right now, you probably have never used a Chinese app. But the reality is if you want to know how the Internet will develop, China, the land once known for its cheap rip offs, has actually become a guide to the future.
But the rest of the video harmonizes the words, visuals and sound track with the production value of an HBO special. As the narrator explains “… that means there is no Facebook, no Twitter and no Google.” We see the logos of three social media Goliaths for a split second …

… before an off-screen bazooka eviscerates the three logos, complete with sound effects.
.
The bulk of the video centers on WeChat described as a “super app.”
.
The pace of the storytelling quickens during the hypothetical scenario of WeChat that goes something like this:
1. Couple at home with a dirty corgi
2. Let’s change this
3. Man shows up to shampoo the corgi
4. Pay for corgi shampoo
5. Post photo of clean corgi
6. Friend sees photo and hires same man to shampoo her poodle
7. Pay for poodle shampoo
8. Friend says thanks and let’s meet at new hip noodle joint
9. Order taxi
10. Order food
11. Pay for food
12. Pet cleaner invests his take in a wealth management product
13. Noodle joint knows when you arrive
14. Posts a review on overcooked meat
The point being, all these varied actions occur within WeChat.
The New York Times video also weaves touches of levity into the story, like calling out the friend who likes Hello Kitty and works at a boring office job as a slacker.
. .
.
You’ll note that the video’s byline carries the names of Jonah M. Kessel and Paul Mozur. While anyone who tracks China on the NYT is familiar with Mozur, Kessel’s name likely won’t ring a bell. He comes from the visual world.
In other words, while the NYT is doing its best to bring its traditional journalists up the visual storytelling curve, the paper is depending on experts in video and filmmaking like Kessel to create industrial-grade video like the one on China changing the internet.
Can we expect this to be the future of newspaper video?
Doubtful.
The reality is that most newspapers don’t have the resources of The New York Times.
Side note: For more on video as a communications tool, I published “Creating a Company Video That Actually Tells a Story” last week.
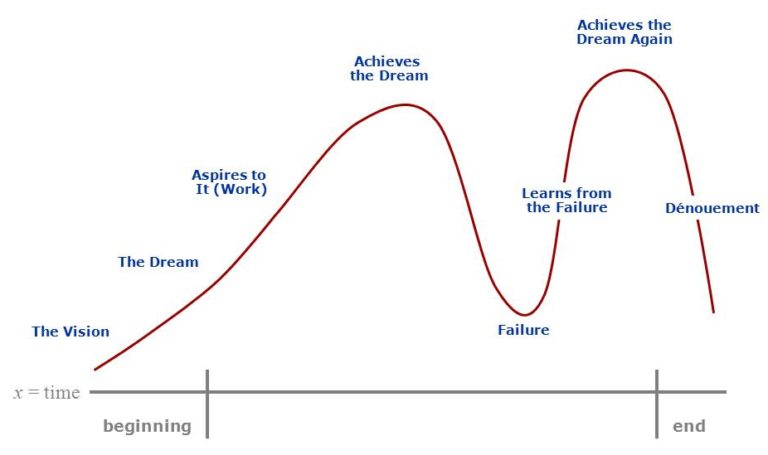




 If you’re pounding out news stories for the Daily Planet, the inverted pyramid serves you well. But applying the inverted pyramid to video isn’t going to hold the viewer’s interest, much less prompt hey-you-gotta-check-this-out sharing across social channels.
If you’re pounding out news stories for the Daily Planet, the inverted pyramid serves you well. But applying the inverted pyramid to video isn’t going to hold the viewer’s interest, much less prompt hey-you-gotta-check-this-out sharing across social channels.


 .
.